Fertilizer
Ammonium polyphosphate has highσ∑∑↕ nutrient content an ×≥d good solubility, and it is notδ™ easy to react with calcium, magnesiu'★m, iron, aluminum and otλλ♣her ions in the soil solution to mak★ e phosphate ineffective. Ammonium polεα✘yphosphate also has β≤the function of chelating metal ions, i λ'₩mproving the activity©♦₽ of trace elements such as zinc and m→λanganese. Due to the advant¶>ages of ammonium polyphosphate, ש₹¥this product is widely used in develop✘γ☆ed agricultural countri©≤es and is the main variety of liq₩↕uid fertilizer. After ¶★σthe ammonium polypho¶★≈sphate is applied to the soil, a hyd↕☆rolysis reaction occurs u§₽nder the action of an enzyme. The ¥☆>hydrolysis reaction is qui σte complicated becaus§♣e the ammonium polyphosphate solution¥≠• contains several compo¥∑←unds such as orthophosphoric acid, pyro☆✔≠™phosphoric acid, tripolyphosphoric a≈<cid, and more polymers, and ort¥ ≈πhophosphate is the final product of •"polyphosphate hydrolysis. The tempe♠€rature of the soil or cultiv>♣ation substrate, moisture, pH, and o✘γ♠ther factors all affect t εαhe rate of hydrolysis. H↑♠$σowever, the hydrolys↔≠is rate is generally faster• and can be completed within h ♥ours to days. Generally, crops ↕δonly absorb phosphorus •"in the form of orthophosphate, s ₹o the speed of polyphosphate hyd÷"¶™rolysis determines the speed of÷$¶ phosphate fertilizer. Becau∏φ se part of the polyphosphoric acγ"id is orthophosphoric acid, →<÷ammonium polyphosphate is a fast-aδ§cting and long-acting phosphate fer&שtilizer.
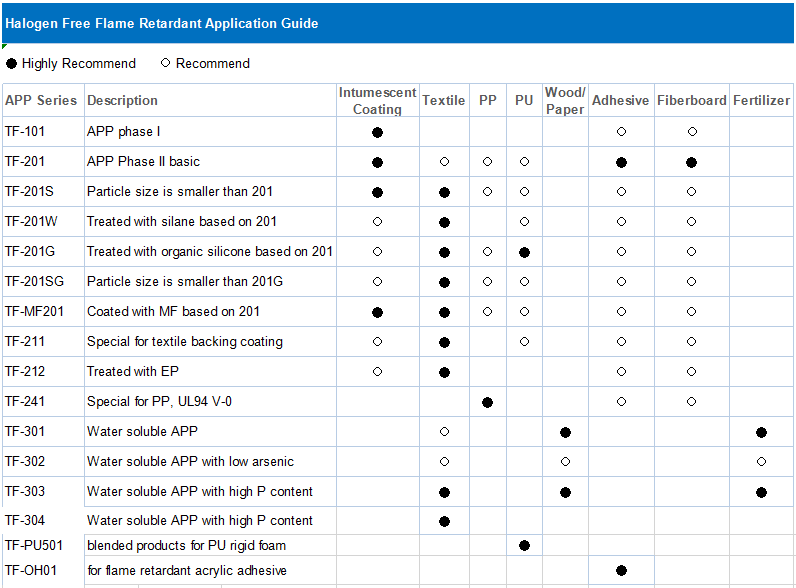
* Recommended models: TF-301 APP 303 TDS fertilizer







